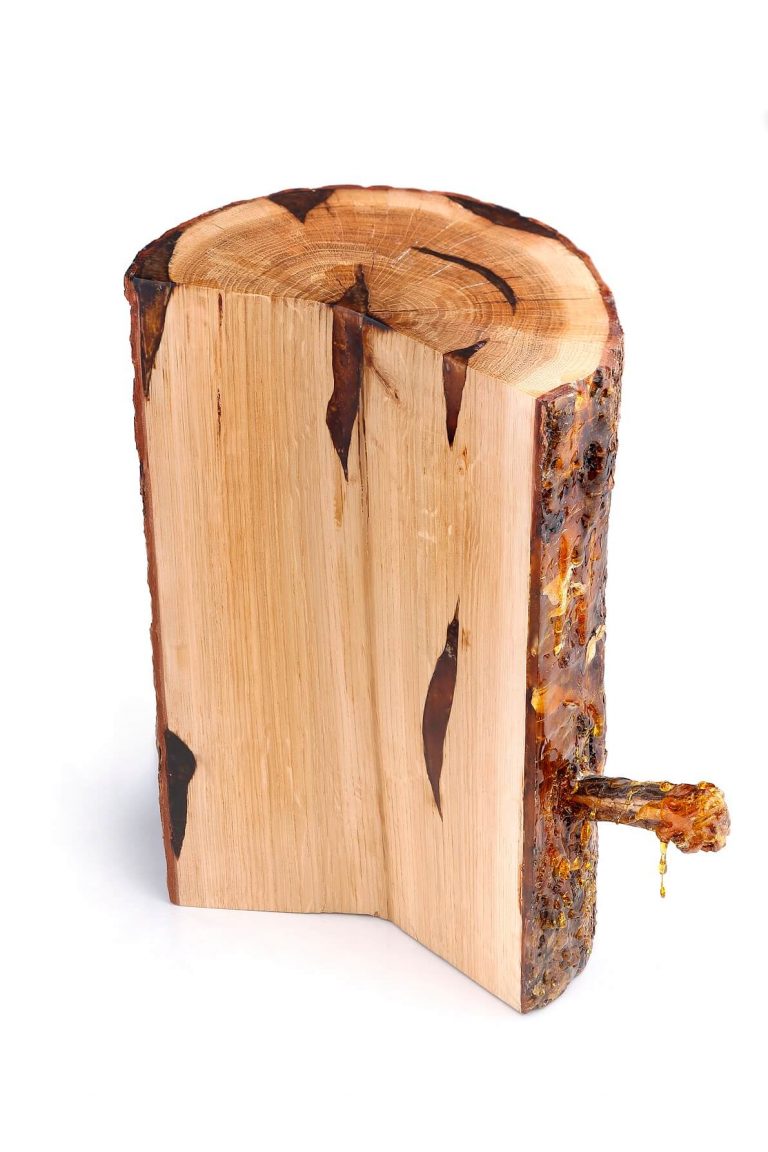
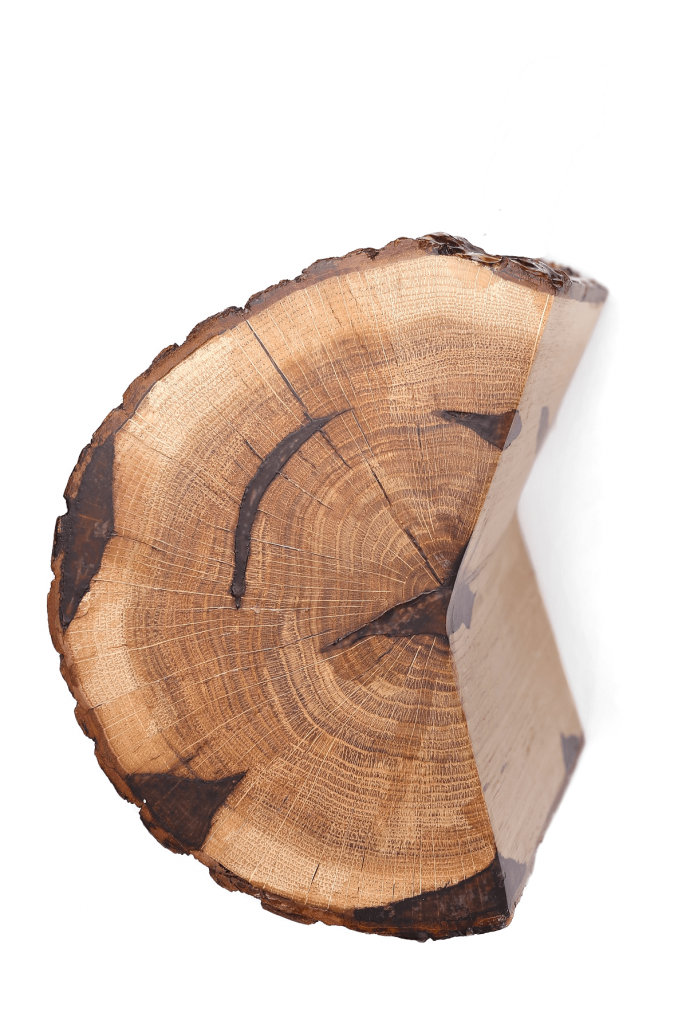
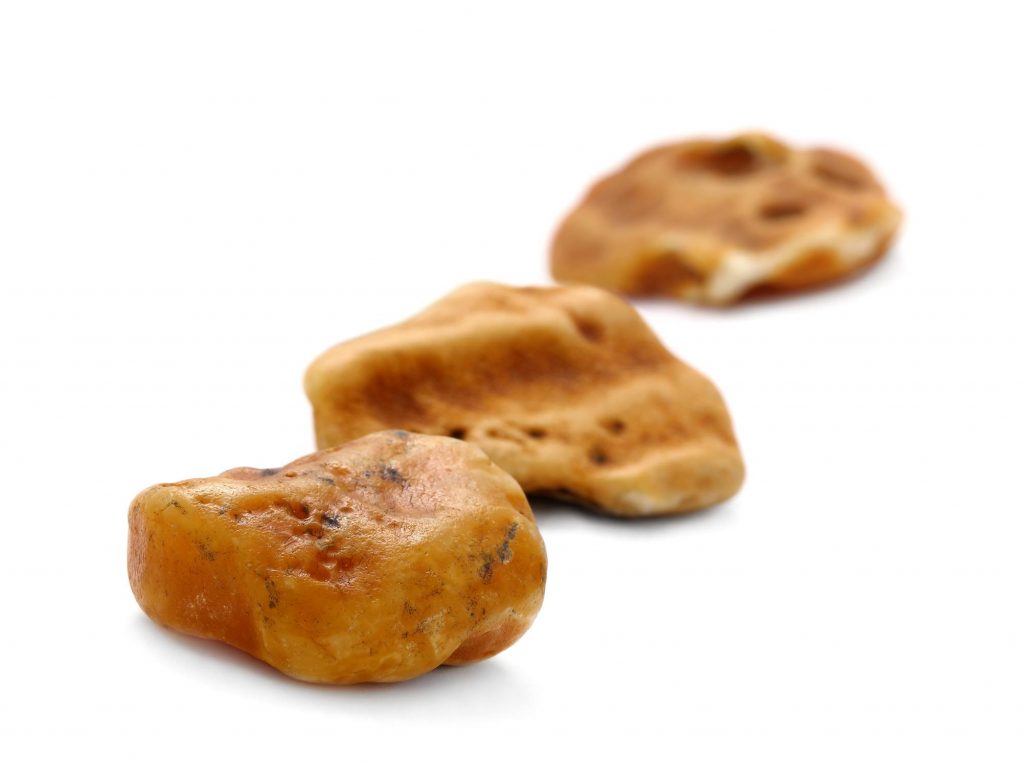
Amber is never found in accidental forms or shapeless.
Amber was produced by resin secretions both inside and outside the tree-trunk.
Natural amber forms depended on:
- where the resin seeped from – inside or outside the tree
- what form the crevice in which it gathered had
- the tree’s age and state of preservation
- the extend of the wound
- the quality of the outflow, affected by the season of the year
- sun exposure
- cracks formed during transport to the deposit
Internal formations
Did not separate from the tree until the wood had decayed.
Types:
- resin pockets – between the annual growth rings
- inter-bark forms – in the tree bark
- under-bark forms – under the tree bark, formations between bark and trunk
- crevice forms – in tree crevices going in various directions
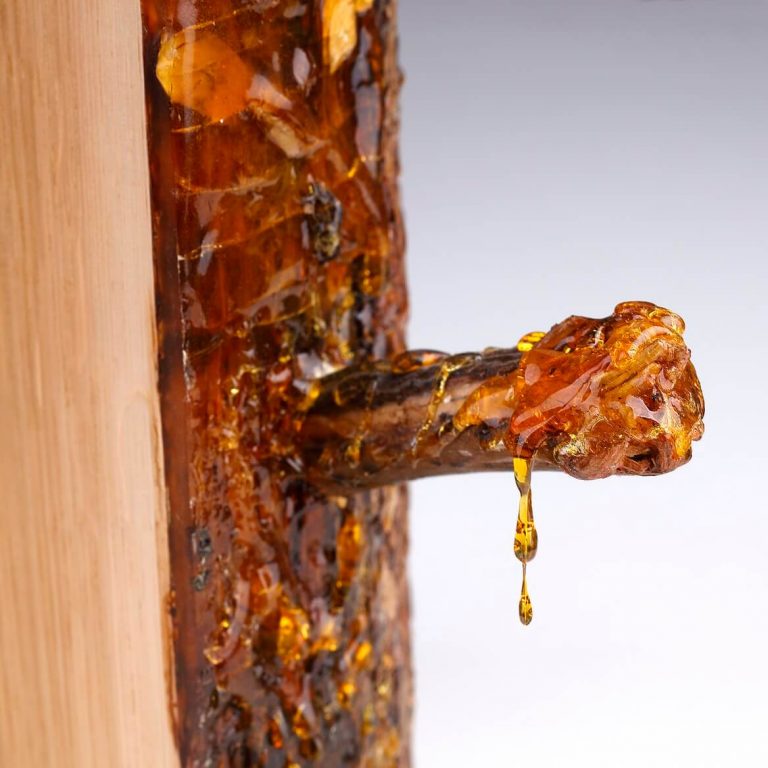
External formations
Are usually transparent. The majority of inclusions are found in these forms.
- drops
- stalactites
- needles
- swellings
- layered amber